Wood chipper machines are essential tools in the fields of forestry, landscaping, and biomass production. They efficiently transform wood and other organic materials into smaller, manageable pieces. However, like any industrial machinery, wood chippers consume energy, making it important to understand this energy consumption for better operational efficiency and cost management. This article explores the energy consumption of wood chipper machines, the factors that influence it, and strategies to optimize energy use.
Understanding Wood Chipper Machines
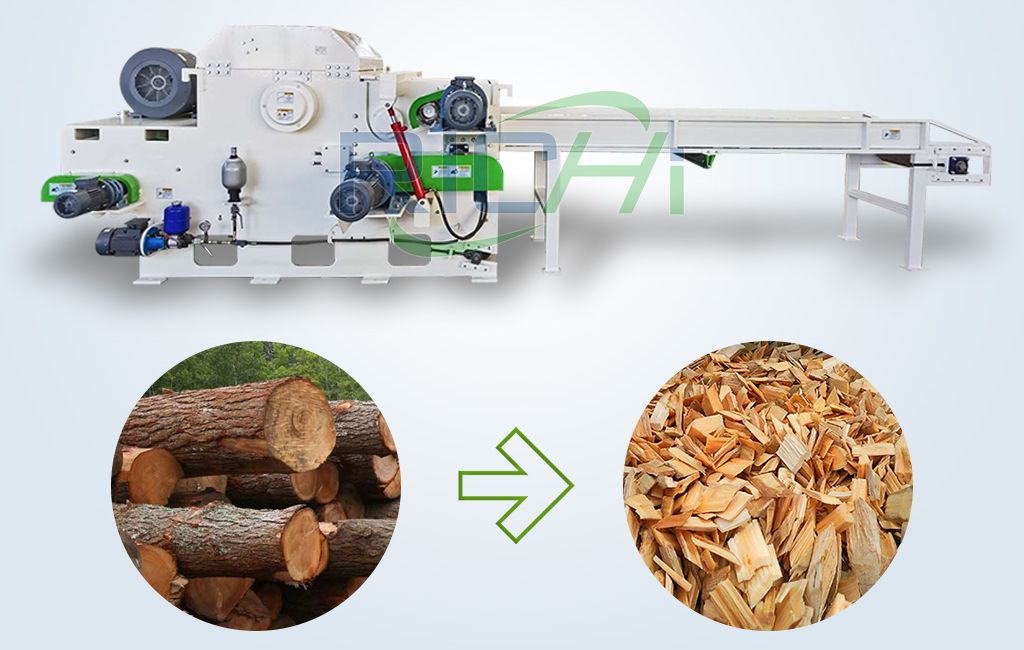
Wood chipper machines come in various types and sizes, each tailored for specific applications. The main categories include:
- Disk Chippers: These machines utilize a large, rotating disk with blades to cut wood into chips, making them suitable for processing smaller branches and twigs.
- Drum Chippers: Featuring a rotating drum with blades, these machines are more powerful and can handle larger logs and branches.
- Screw Chippers: These machines employ a large screw to pull in and chip wood material, often used for specialized industrial applications.
Each type of chipper has its unique mechanism and energy requirements, affecting overall energy consumption. (Related post: wood chip hammer mill)

Factors Influencing Energy Consumption
Several key factors affect the energy consumption of wood chipper machines:
- Machine Type and Size: Larger, industrial-grade chippers typically consume more energy than smaller, residential models due to their higher capacity and power requirements. For example, drum chippers generally consume more energy than disk chippers, as they are designed for more demanding tasks.
- Engine Power: The engine power, measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW), directly impacts energy consumption. Higher horsepower engines use more fuel or electricity. For instance, the Vermeer BC2100XL Tier 4 Final Brush Chipper, with a 275 HP engine, consumes significantly more energy than the smaller BC700XL Brush Chipper with a 25 HP engine.
- Material Type and Condition: The type and condition of the wood being processed—such as whether it is green or dry, or whether it is hardwood or softwood—affect the energy needed for chipping. Hardwoods and green wood are more difficult to chip and require more energy, while dry softwood branches consume less energy compared to wet hardwood logs.
- Feed Rate and Speed: The rate at which material is fed into the chipper and the speed of the rotating blades or drum impact energy consumption. Higher feed rates and faster speeds typically lead to increased energy usage. Operators can adjust feed rates to manage energy consumption based on the material being processed.
- Operational Efficiency: Well-maintained machines with sharp blades and properly calibrated settings operate more efficiently and consume less energy. Regular maintenance, including blade sharpening and engine tuning, is crucial for optimal energy performance.
Measuring Energy Consumption
Energy consumption in wood chipper machines can be measured in different ways, depending on the power source:
- Fuel Consumption (for Gasoline or Diesel Engines): This is typically measured in gallons per hour (GPH) or liters per hour (LPH). For example, a high-capacity drum chipper might consume 5-10 gallons of diesel per hour, depending on the workload.
- Electricity Consumption (for Electric Chippers): This is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). An electric wood chipper with a 10 kW motor running for one hour consumes 10 kWh of electricity.
Optimizing Energy Consumption
To enhance energy efficiency and reduce operational costs, consider the following strategies:
- Choose the Right Machine: Select a wood chipper that fits the scale and type of your operations. Using an overpowered machine can lead to unnecessary energy consumption, while an underpowered machine may struggle, causing inefficiency and increased energy use. For example, a residential user might opt for a smaller, less powerful chipper, while a commercial operation may require a high-capacity drum chipper.
- Regular Maintenance: Keeping the machine well-maintained ensures efficient operation. Regularly sharpening blades, checking engine performance, and replacing worn parts can significantly reduce energy consumption by ensuring the machine runs at peak efficiency.
- Optimize Feed Rate: Adjust the feed rate according to the material being processed. Feeding material too quickly can overload the machine and increase energy consumption. Utilize the chipper’s feed control system, if available, to optimize the feed rate and minimize energy use.
- Use Energy-Efficient Models: Consider investing in newer, energy-efficient models that incorporate advanced technologies designed to reduce energy consumption. For instance, Vermeer’s brush chippers feature the EcoIdle™ engine control system, which saves fuel and reduces noise by automatically lowering engine speed after periods of inactivity.
- Monitor and Analyze Energy Use: Implement monitoring tools to track energy consumption and identify areas for improvement. Analyzing energy use patterns can help optimize operations and reduce costs. A monitoring system can provide real-time data on fuel or electricity consumption, enabling operators to make informed decisions.
Case Study: Vermeer Brush Chippers
Vermeer’s brush chippers are designed with features that enhance efficiency and operator safety. Their SmartFeed feed-sensing control improves productivity by optimizing the processing of hardwood, while the EcoIdle™ engine control system saves fuel and reduces noise by automatically lowering engine speed after one or five minutes of inactivity.
For instance, the Vermeer BC2100XL Tier 4 Final Brush Chipper, equipped with a 275 HP engine, is tailored for large-scale operations and integrates advanced features to optimize energy use. Despite its powerful engine, the machine’s efficient design and control systems effectively manage energy consumption.
Environmental Considerations
Optimizing energy consumption in wood chipper machines also offers environmental benefits:
- Reduced Emissions: Lower fuel consumption leads to decreased greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Electric chippers, when powered by renewable energy sources, provide an environmentally friendly alternative to gasoline or diesel-powered models.
- Sustainable Operations: Efficient energy use supports sustainable forestry and landscaping practices by minimizing resource waste and environmental impact. Implementing energy-efficient practices aligns with broader sustainability goals and enhances the reputation of businesses committed to environmental stewardship.
Conclusion
Understanding and optimizing the energy consumption of wood chipper machines is essential for efficient and cost-effective operations. By selecting the appropriate machine, maintaining it properly, adjusting feed rates, and utilizing energy-efficient models, operators can significantly lower energy usage and operational costs.
Manufacturers like Vermeer offer advanced wood chippers equipped with features designed to improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption. By leveraging these technologies and implementing best practices, businesses and individuals can achieve sustainable and efficient wood chipping operations, leading to both economic and environmental benefits.
For details please contact: Richi Machinery
WhatsApp:86 138 3838 9622
Email:enquiry@richipelletmachine.com